Hypermobility in Children

Written on October 29, 2021
What is Hypermobility?
Hypermobility is a term used to describe joints that move more than normal and can place the joints in increased stress.
How can Hypermobility affect my child?
Risk of Injury
Increased joint movement can cause joints, ligaments, and tendons to be at higher risk of injury. Joints are less stable and can strain all the structures attempting to make the joint more stable. In addition to joints moving more than normal the signals to the brain about where the body is in space can be impaired due to the ligaments requiring increased stretch before the message is sent to the brain making it harder for children to know where they are in space and making it harder for them to correct the joint position prior to exposure to extremes of range of motion.
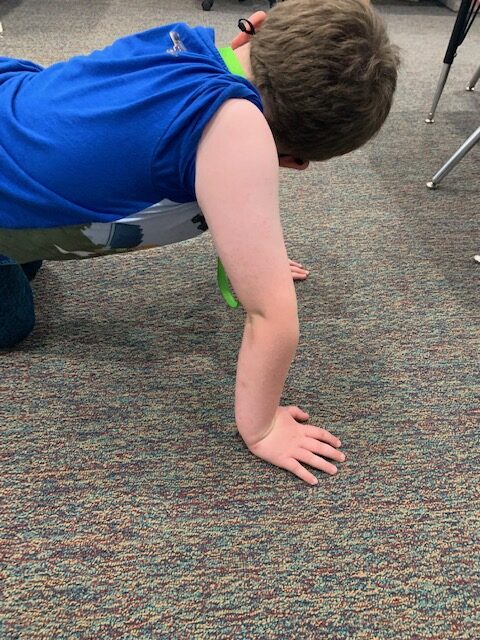
What are the common signs of hypermobility in children?
| Knee Hyperextension | Elbow Hyperextension | Hands to the Floor with Straight Knees | Flat Feet |
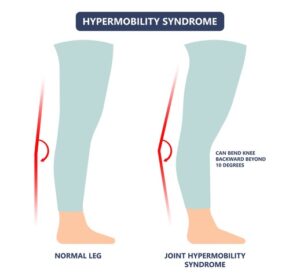 |  |  |  |
NOTE: These are all postures that can occur in typically developing children with no cause for concern. However, when multiple joints are impacted and your child twists their ankles or knees frequently, or reports leg pain this may be a sign to follow-up with your physician.
Who can help my child?
BDI Pediatric Physical Therapists create a strengthening and proprioception program that can improve your child’s participation in recreational activities as well as lower their risk of injuries. Exercises consist of
- strengthening the muscles around the joints
- working on postural control
- sport specific training
Next Steps
Do you think your child is at risk for injury due to hypermobility? Schedule a free screening with one of our pediatric physical therapists. When hypermobility is identified and treated with a proper development regimen, your child will report less pain, improve balance, strength, and functional performance. In addition, your child can prevent future pain.
Written by: Lisa M. Wood, PT, DPT
